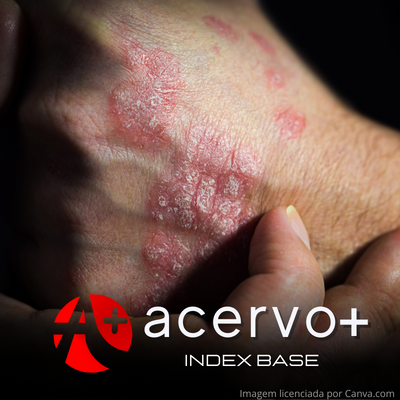
Uma abordagem geral da Psoríase: revisão de literatura
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Resumo
Objetivo: Analisar as características da Psoríase. Revisão bibliográfica: A psoríase é uma doença sistêmica crônica imunomediada que afeta aproximadamente 100 milhões de pessoas em todo o mundo. A doença parece ser o resultado de uma interação desregulada entre células imunes, queratinócitos da pele e o ambiente, levando a um processo inflamatório persistente modulado por células T ativadas e citocinas pró-inflamatórias. A psoríase está associada ao aumento do risco de comorbidades, incluindo, mas não limitado a artrite psoriática, doença cardiovascular, diabetes mellitus, obesidade, doença inflamatória intestinal e doença hepática gordurosa não alcoólica em comparação com a população em geral. Considerações finais: A psoríase é um problema de saúde pública global, sendo uma doença inflamatória sistêmica crônica da pele com forte predisposição genética e traços patogênicos autoimunes. Seu tratamento em casos leves é realizado com agentes tópicos como por exemplo, Calcipotriol, Inibidores de Calcineurina, Tretinoína, glicocorticóide e fototerapia. Já em casos moderados a graves utiliza-se terapias sistêmicas convencionais como o Metorexato, a Ciclosporina e Acitretina, além de biológicos que podem ser usados na falha das terapias convencionais.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright © | Todos os direitos reservados.
A revista detém os direitos autorais exclusivos de publicação deste artigo nos termos da lei 9610/98.
Reprodução parcial
É livre o uso de partes do texto, figuras e questionário do artigo, sendo obrigatória a citação dos autores e revista.
Reprodução total
É expressamente proibida, devendo ser autorizada pela revista.
Referências
2. DAND N, et al. Psoriasis and Genetics. Acta Derm Venereol, 2020; 100(3): adv00030.
3. DOPYTALSKA K, et al. The Role of Epigenetic Factors in Psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci, 2021; 22(17): 9294.
4. FERRELI C, et al. Histopathological aspects of psoriasis and its uncommon variants. G Ital Dermatol Venereol, 2018; 153(2): 173-184.
5. FU Y, et al. Association of Psoriasis With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol, 2018; 154(12): 1417-1423.
6. GIROLOMONI G, et al. The role of IL-23 and the IL-23/TH 17 immune axis in the pathogenesis and treatment of psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2017; 31(10): 1616-1626.
7. GRAN F, et al. Current Developments in the Immunology of Psoriasis. Yale J Biol Med, 2020; 93(1): 97-110.
8. KAMATA M e TADA Y. Efficacy and Safety of Biologics for Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis and Their Impact on Comorbidities: A Literature Review. Int J Mol Sci, 2020; 21(5): 1690.
9. KAMIYA K, et al. Risk Factors for the Development of Psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci, 2019; 20(18): 4347.
10. KORMAN NJ. Management of psoriasis as a systemic disease: what is the evidence? Br J Dermatol, 2020; 182(4): 840-848.
11. MASSON W, et al. Psoriasis and Cardiovascular Risk: A Comprehensive Review. Adv Ther, 2020; 37(5): 2017-2033.
12. MEROLA JF, et al. Underdiagnosed and undertreated psoriasis: Nuances of treating psoriasis affecting the scalp, face, intertriginous areas, genitals, hands, feet, and nails. Dermatol Ther, 2018; 31(3): e12589.
13. OGAWA K e OKADA Y. The current landscape of psoriasis genetics in 2020. J Dermatol Sci, 2020; 99(1): 2-8.
14. OLEJNICZAK-STARUCH I, et al. Alterations of the Skin and Gut Microbiome in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci, 2021; 22(8): 3998.
15. OSMANCEVIC A e STAHLE M. Treatment of psoriasis: before and now. Lakartidningen, 2017; 114: EU6Y.
16. PETIT RG, et al. Psoriasis: From Pathogenesis to Pharmacological and Nano-Technological-Based Therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci, 2021; 22(9): 4983.
17. REID C e GRIFIFITHS CEM. Psoriasis and Treatment: Past, Present and Future Aspects. Acta Derm Venereol, 2020; 100(3): adv00032.
18. RENDON A e SCHAKEL K. Psoriasis Pathogenesis and Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(6): 1475.
19. RONHOLT K e IVERSEN L. Old and New Biological Therapies for Psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci, 2017; 18(11): 2297.
20. ROSZKIEWICZ M, et al. Environmental risk factors and epigenetic alternations in psoriasis. Ann Agric Environ Med, 2020; 27(3): 335-342.
21. SINGH R, et al. The Cytokine Mediated Molecular Pathophysiology of Psoriasis and Its Clinical Implications. Int J Mol Sci, 2021; 22(23): 12793.
22. SU W, et al. Exploring the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis Complicated With Atherosclerosis via Microarray Data Analysis. Front Immunol, 2021; 12: 667690.
23. TOKUYAMA M e MABUCHI T. New Treatment Addressing the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci, 2020; 21(20): 7488.
24. YANG K, et al. Use of IL-23 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Plaque Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Comprehensive Review. Am J Clin Dermatol, 2021; 22(2): 173-192.
25. ZHANG P e WU MX. A clinical review of phototherapy for psoriasis. Lasers Med Sci, 2018; 33(1): 173-180.