Efeito nefroprotetor da nanoemulsão de óleo de Cannabis sativa em ratos expostos ao ácido valpróico durante o período intrauterino
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Resumo
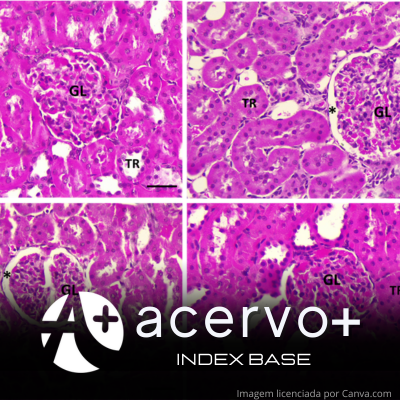
Objetivo: Avaliar os efeitos terapêuticos da nanoemulsão de óleo de Cannabis sativa (CBDON) nas alterações renais induzidas pelo ácido valproico (VPA) em ratos. Métodos: Fêmeas grávidas de ratas Wistar foram expostas ao VPA, e seus filhotes receberam tratamento com nanoemulsão de CBD nas concentrações de 1% e 2%. Após 60 dias, avaliações foram feitas por meio de biometria corporal, morfometria renal e análises de estresse oxidativo, com quantificação de malondialdeído (MDA) e atividade de enzimas antioxidantes. Os dados foram analisados por estatística descritiva e inferencial. Resultados: O VPA causou redução no peso corporal e alterações nas estruturas renais, como diminuição da área e diâmetro glomerular. O tratamento com a nanoemulsão de CBD, especialmente na concentração de 2%, mostrou um efeito positivo na recuperação dos parâmetros morfométricos renais e na redução do estresse oxidativo, revertendo parcialmente os danos causados pelo VPA. Foi observado aumento na atividade de enzimas antioxidantes e diminuição do MDA nos grupos tratados com CBD. Conclusão: O estudo sugere que a nanoemulsão de CBD pode ter um efeito nefroprotetor, mitigando as alterações renais induzidas pelo VPA durante durante o período intrauterino.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
Copyright © | Todos os direitos reservados.
A revista detém os direitos autorais exclusivos de publicação deste artigo nos termos da lei 9610/98.
Reprodução parcial
É livre o uso de partes do texto, figuras e questionário do artigo, sendo obrigatória a citação dos autores e revista.
Reprodução total
É expressamente proibida, devendo ser autorizada pela revista.
Referências
2. ADEWOLE KE, et al. Exploring phytotherapeutic approach in the management of valproic acid-induced toxicity. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2021; 1–21.
3. AGUILAR S et al. Pregnancy and Epilepsy. Acta Obstet Ginecol Port, Coimbra, 2016; 10 (2):120-129.
4. ALSDORF, Rachel; WYSZYNSKI, Diego F. Teratogenicity of sodium valproate. Expert opinion on drug safety, v. 4, n. 2, p. 345-353, 2005.
5. ANGUISSOLA, Giulia et al. Kidney tubular injury induced by valproic acid: systematic literature review. Pediatric Nephrology, v. 38, n. 6, p. 1725-1731, 2023.
6. BARRETO LAAS. A maconha (Cannabis sativa) e seu valor terapêutico. 2002. Monografia [Trabalho de conclusão do curso de graduação em Ciências Biológicas] apresentada à Faculdade de Ciências da Saúde do Centro Universitário de Brasília. Brasília, 2002.
7. BENZIE IF, STRAIN JJ. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Analytical biochemistry, 1996; 239(1): 70-76.
8. BHATTACHARYYA A. et al., Oxidative stress: an essential factor in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal mucosal diseases. Physiological reviews, 2014; 94(2): 329-354.
9. BITON V. Effect of antiepileptic drugs on bodyweight: overview and clinical implications for the treatment of epilepsy. CNS Drugs, 2003;17(11):781-91.
10. BRACONNIER, L et al. Encéphalopathie hyperammoniémique en Réanimation adulte: à propos de deux observations cliniques. Médecine Intensive Réanimation, 2018; 27: 558–562.
11. CHEN, O.; The early overgrowth theory of autism spectrum disorder: insight into convergent mechanisms from valproic acid exposure and translational models. Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science, 2020; 173: 275-300.
12. CHUA JT. Et al. Endocannabinoid system and the kidneys: from renal physiology to injury and disease. Cannabis and cannabinoid research, 2019; 4(1): 10-20.
13. CUPERTINO MC, et al. Long-lasting morphofunctional remodelling of liver parenchyma and stroma after a single exposure to low and moderate doses of cadmium in rats. Int. J. Exp. Pathol, 2013; 94, 343–351.
14. MELLO PA et al. Nefrotoxicidade e alterações de exames laboratoriais por fármacos: revisão da literatura. Revista de Medicina, 2021; 100 (2); 152-161.
15. FERREIRA ALA, MATSUBARA LS. Radicais livres: conceitos, doenças relacionadas, sistema de defesa e estresse oxidativo. RAMB, 1997; 43(1):61-8.
16. GAD AM. Study on the influence of caffeic acid against sodium valproate–induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Journal of biochemical and molecular toxicology, 2018; 32 (8); e22175.
17. GAYAM V. et al. Valproic acid induced acute liver injury resulting in hepatic encephalopathy-a case report and literature review. Journal of Community Hospital Internal Medicine Perspectives, 2018; 8 (5): 311-314.
18. GASTON TE, FRIEDMAN D. Pharmacology of cannabinoids in the treatment of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav, 2017; May:313-318.
19. GILLHAM B. et al., Wills’: Biochemical basis of medicine, 3rd ed., Butterworth- Heinemann: Oxford, 1997.
20. GUTTERRIDGE JMC, HALLIWELL B. The measurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation in biological systems. Trends Biochem. Sci, 1990; 15: 129–135.
21. HABIG WH, et al. Glutathione S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. Journal of biological Chemistry, 1974; 249 (22): 7130-7139.
22. HALL AM, et al. Síndrome de Fanconi renal induzida por drogas . QJM, 2014; 107: 261 – 269.
23. HAMED SA. The effect of antiepileptic drugs on the kidney function and structure. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology, 2017; 10 (9): 993-1006.
24. HEIDARI R, et al., Mechanism of valproic acid-induced Fanconi syndrome involves mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in rat kidney. Nephrology (Carlton), 2018 Apr;23(4):351-361.
25. HONÓRIO KM, et al. Aspectos terapêuticos de compostos da planta Cannabis sativa. Química nova, 2006; 29 (2): 318-325.
26. LOWRY OH, et al. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. Anal. Biochem. 1951; 193, 265–275.
27. MATTOS BSm et al. Quercetin prevents alterations of behavioral parameters, delta-aminolevulinic dehydratase activity, and oxidative damage in brain of rats in a prenatal model of autism. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 2020; 80: 287-302.
28. MCGARIGAL K. et al. Ordenação: análise de componentes principais. Estatística multivariada para pesquisa em ecologia e vida selvagem , p. 19-80, 2000.
29. MONCADA SMRJ, et al. Nitric oxide: pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev, 1991; 43: 109–142.
30. ORNOY A. et al. S-adenosyl methionine prevents ASD like behaviors triggered by early postnatal valproic acid exposure in very young mice. Neurotoxicology and Teratology. Amsterdã, 2019; 71: 64-74.
31. PECOITS-FILHO, R. Diagnóstico de doença renal crônica: avaliação da função renal. J Bras Nefrol,2004; 26 (3): 4-5.
32. PERUCCA E. Pharmacological and therapeutic properties of valproate: a summary after 35 years of clinical experience. CNS drugs, 2002; 16: 695-714.
33. POLZIN DJ. Chronic kidney disease in small animals. Vet Clin Small Anim, 2011; 41:15-30.
34. REMUZZI G, et al. Mechanisms of progression and regression of renal lesions of chronic nephropathies and diabetes. The Journal of clinical investigation, v. 116, n. 2, p. 288-296, 2006.
35. SAFDAR A, ISMAIL F. A comprehensive review on pharmacological applications and drug-induced toxicity of valproic acid. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 2023; 31 (2): 265-278.
36. SCHNEIDER CD, OLIVEIRA AR. Radicais livres de oxigênio e exercício: mecanismos de formação e adaptação ao treinamento físico. RBME. 2004; 10(10):308-13.
37. SIDDIQUI IA, et al. Protective effects of black tea extract on testosterone induced oxidative damage in prostate. Cancer Lett. 2005; 227: 125–132.
38. TAN L, et al. The influence of cytochrome oxidase CYP2A6, CYP2B6, and CYP2C9 polymorphisms on the plasma concentrations of valproic acid in epileptic patients. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg, 2010; 112, 320–323.
39. URSO ML, CLARKSON PM. Oxidative stress, exercise, and antioxidant supplementation. Toxicology, 2003; 189(1-2), 41-54.
40. ZHU MM, et al. The pharmacogenomics of valproic acid. Journal of human genetics, 2017; 62(12), 1009-1014.
41. Ricart-Jané D, et al. Anticoagulants and other preanalytical factors interfere in plasma nitrate/nitrite quantification by the Griess method. Nitric Oxide - Biology and Chemistry, 2002; 6: 178–185